Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wang, Q.*; Ma, N.*; Huang, W.*; Shi, J.*; Luo, X.-T.*; Tomitaka, Sora*; Morooka, Satoshi; Watanabe, Makoto*
Materials Research Letters (Internet), 11(9), p.742 - 748, 2023/09
Tokunaga, Sho; Horiguchi, Hironori; Nakamura, Takemi
JAEA-Technology 2023-001, 37 Pages, 2023/05
The cold neutron source (CNS) of the research reactor JRR-3 converts thermal neutrons generated in the reactor into low-energy cold neutrons by moderating them with liquid hydrogen stored in the moderator cell. Cold neutrons generated by the CNS are transported to experimental instruments using neutron conduits, and are used for many studies of physical properties, mainly in life science, polymer science, environmental science, etc. Improvement of cold neutron intensity is essential to maintain competitiveness with the world's research reactors in neutron science, and we are developing a new CNS that incorporates new knowledge. The current moderator cell for the CNS of JRR-3 is a stainless-steel container which is a canteen bottle type, and the cold neutron intensity can be improved by changing the material and shape. Therefore, the basic specifications of the new moderator cell were changed to aluminum alloy which has a smaller neutron absorption cross section, and the shape was optimized using a Monte Carlo code MCNP. Since these changes in specifications will result in changes in heat generation and heat transfer conditions, the CNS of JRR-3 was re-evaluated in terms of self-regulating characteristic, heat transport limits, heat resistance and pressure resistance, etc., to confirm its feasibility in thermal-hydraulic design. This report summarizes the results of the thermal-hydraulic design evaluation of the new moderator cell.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Yan, M.*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Nanomaterials (Internet), 13(1), p.76_1 - 76_9, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:71.03(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)To enhance neutron intensity below cold neutrons, it is proposed that nanosized graphene aggregation could facilitate neutron coherent scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamond. It might also be possible to use it in high neutron radiation conditions due to graphene's strong sp2 bonds. Using the RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source and iMATERIA at J-PARC, we performed neutron measurement experiments, total neutron cross-section, and small-angle neutron scattering on nanosized graphene aggregation. The measured data revealed, for the first time, that nanosized graphene aggregation increased the total cross-sections and small-angle scattering in the cold neutron energy region, most likely due to coherent scattering, resulting in higher neutron intensities, similar to nanodiamond.
Nakashio, Nobuyuki*; Osugi, Takeshi; Kurosawa, Shigenobu; Ishikawa, Joji; Hemmi, Ko; Iketani, Shotaro; Yokobori, Tomohiko
JAEA-Technology 2022-016, 47 Pages, 2022/08
The Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started operation of the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVWF) for production of waste packages for disposal of low-level radioactive solid wastes (LLW). To clarify the operating conditions for homogenization of non-metallic LLW, preliminary tests were carried out using the plasma melting furnace of the non-metal melting unit. The fluidity of molten waste influences homogenization conditions of solidified products. It was clarified that the viscosity, which is determined by the chemical composition and the melting temperature, influence the fluidity of molten waste greatly through previous literature review and the small-scale melting tests. In the preliminary tests, the simulated waste with a cold tracer loaded in 200 L drums were melted. Using the waste chemical components (basicity, iron oxide concentration) as an experimental parameter, the homogeneity of the chemical components of the solidified product was investigated and the homogenization conditions of melting tests were examined. The retention ratio of the tracer in the molten bath was also confirmed. The viscosity of the molten wastes was measured and the correlation with homogeneity was examined. In addition, the technical requirements that should be concerned in advance for future actual operation were discussed.
Nishida, Satoru*; Nishino, Soichiro*; Sekine, Masahiko*; Oka, Yuki*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Morii, Yukio*; Ishii, Yoshinobu*
Materials Transactions, 62(5), p.667 - 674, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ma, B.*; Teshigawara, Makoto; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yan, M.*; Hashiguchi, Takao*; Yamagata, Yutaka*; Wang, S.*; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Otake, Yoshie*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 995, p.165079_1 - 165079_7, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:33.7(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have optimized a cold neutron moderator to be operated at the RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source. We selected a safe and easy to manage material, mesitylene, as the RANS cold moderator. An efficient moderator system was designed by studying and optimizing a coupled cold neutron moderator of mesitylene at 20 K with a polyethylene (PE) pre-moderator at room temperature in the slab geometry with Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) simulations. The parameters of mesitylene and PE thickness, the reflector, and the shielding configuration were studied to increase cold neutron intensities. Consequently, an integrated cold neutron intensity of 1.15 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /
/ A at 2 m from the neutron-producing target was finally achieved, which was 12 times higher than that of the current PE moderator. The results showed attractive application prospect of mesitylene as cold neutron moderator material.
A at 2 m from the neutron-producing target was finally achieved, which was 12 times higher than that of the current PE moderator. The results showed attractive application prospect of mesitylene as cold neutron moderator material.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-019, 58 Pages, 2021/01
An experiment denoted as SB-SL-01 was conducted on March 27, 1990 using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in the Rig of Safety Assessment-IV (ROSA-IV) Program. The ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-SL-01 simulated a main steam line break (MSLB) accident in a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The test assumptions were made such as auxiliary feedwater (AFW) injection into secondary-side of both steam generators (SGs) and coolant injection from high pressure injection (HPI) system of emergency core cooling system into cold legs in both loops. The MSLB led to a fast depressurization of broken SG, which caused a decrease in the broken SG secondary-side wide-range liquid level. The broken SG secondary-side wide-range liquid level recovered because of the AFW injection into the broken SG secondary-side. The primary pressure temporarily decreased a little just after the MSLB, and increased up to 16.1 MPa following the closure of the SG main steam isolation valves. Coolant was manually injected from the HPI system into cold legs in both loops a few minutes after the primary pressure reduced to below 10 MPa. The primary pressure raised due to the HPI coolant injection, but was kept at less than 16.2 MPa by fully opening a power-operated relief valve of pressurizer. The core was filled with subcooled liquid through the experiment. Thermal stratification was seen in intact loop cold leg during the HPI coolant injection owing to the flow stagnation. On the other hand, significant natural circulation prevailed in broken loop. When the continuous core cooling was ensured by the successive coolant injection from the HPI system, the experiment was terminated. The experimental data obtained would be useful to consider recovery actions and procedures in the multiple fault accident with the MSLB of PWR. This report summarizes the test procedures, conditions, and major observations in the ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-SL-01.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke*; Ichikawa, Go*; Takata, Shinichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Harada, Masahide; Oi, Motoki; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Kai, Tetsuya; Kawamura, Seiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 929, p.113 - 120, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:87.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)A nano-diamond is an attractive neutron reflection material below cold neutron energy. The total neutron cross section of a nano-diamond was derived from a neutron transmission measurement over the neutron energy range of 0.2 meV to 100 meV because total neutron cross section data were not available. The total cross section of a nano-diamond with particle size of approximately 5 nm increased with a decrease in neutron energy to 0.2 meV. It was approximately two orders of magnitude larger than that of graphite at 0.2 meV. The contribution of inelastic scattering to the total cross section was to be shown negligible small at neutron energies of 1.2, 1.5, 1.9, 2.6, and 5.9 meV in the inelastic neutron scattering measurement. Moreover, small-angle neutron scattering measurements of the nano-diamond showed a large scattering cross section in the forward direction for low neutron energies.
Tamura, Itaru
Hamon, 28(4), p.204 - 207, 2018/11
A Neutron guide is one of the devices to transport neutron beam for long distance without sacrificing much neutrons; therefore, it can supply neutrons to many experimental instruments distributed in a large experimental hall. Also, by using a curved guide, only the neutrons in a required energy range can be transported, and  rays and fast neutrons can be effectively eliminated, therefore the signal to background ratio is improved. In addition, a neutron beam can be branched by applying curved guides. Neutron guides are also used to control the divergence angle and intensity of the neutron beam supplied to the neutron instrument.
rays and fast neutrons can be effectively eliminated, therefore the signal to background ratio is improved. In addition, a neutron beam can be branched by applying curved guides. Neutron guides are also used to control the divergence angle and intensity of the neutron beam supplied to the neutron instrument.
Takeda, Takeshi; Otsu, Iwao
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 109, p.9 - 21, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Shigeo*; Shobu, Takahisa; Sato, Kozue*; Ogawa, Hiromi*; Wagatsuma, Kazuaki*; Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Tashiro, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Shigeru*
ISIJ International, 55(7), p.1432 - 1438, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:53.65(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To characterize the distribution and anisotropy of dislocations in cold-drawn pearlitic steel wires, X-ray diffraction line-profile analysis was performed using synchrotron radiation micro-beams. The plastic shear strain was generally more severe near the surface than the center of the wire, whereas the dislocation density distribution was almost constant from the center to the surface. On the other hand, the dislocation rearrangement, which evolves the dislocation cell structure, progressed closer to the surface. It was also revealed that a difference between the hardness in axial and transverse wire directions could be explained by anisotropic dislocation density. Line-profile analysis based on diffraction data at elevated temperatures was performed. Whereas the cementite recovery progressed at a constant rate, the ferrite phase recovery rate was temperature-dependent, suggesting that the ferrite phase recovery was less related to that of the cementite phase.
Arai, Masaji; Tamura, Itaru; Hazawa, Tomoya
JAEA-Technology 2015-010, 52 Pages, 2015/05
In the Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, developments of high-performance CNS moderator vessel that can produce cold neutron intensity about two times higher compared to the existing vessel have been performed in the second medium term plans. We compiled this report about the technological development to solve several problems with the design and manufacture of new vessel. In the present study, design strength evaluation, mockup test, simulation for thermo-fluid dynamics of the liquid hydrogen and strength evaluation of the different-material-bonding were studied. By these evaluation results, we verified that the developed new vessel can be applied to CNS moderator vessel of JRR-3.
Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Tsukamoto, Takuya*; Kawai, Hirokazu*; Miura, Setsuo*; Zhang, S.*; Shobu, Takahisa; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Materials Science Forum, 777, p.176 - 181, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oyama, Yukio; Ikeda, Yujiro
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (107), p.45 - 51, 2005/09
JAERI and KEK are jointly conducting high intensity proton accelerator project (J-PARC). The outline of the J-PARC project and a design concept of the neutron source facility at J-PARC are described in detail.
Minehara, Eisuke; Hajima, Ryoichi; Iijima, Hokuto; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Nagai, Ryoji; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Nishitani, Tomohiro; Sawamura, Masaru; Yamauchi, Toshihiko
Proceedings of 27th International Free Electron Laser Conference (FEL 2005) (CD-ROM), p.305 - 308, 2005/00
The JAERI high power ERL-FEL has been extended to the more powerful and efficient free-electron laser (FEL) than 10kW for nuclear energy industries, and other heavy industries like defense, shipbuilding, chemical industries, environmental sciences, space-debris, and power beaming and so on. In order to realize such a tunable, highly-efficient, high average power, high peak power and ultra-short pulse FEL, we need the efficient and powerful FEL driven by the JAERI compact, stand-alone and zero boil-off super-conducting RF linac with an energy-recovery geometry. Our discussions on the ERL-FEL will cover the current status of the 10kW upgrading and its applications of non-thermal peeling, cutting, and drilling to decommission the nuclear power plants, and to demonstrate successfully the proof of principle prevention of cold-worked stress-corrosion cracking failures in nuclear power reactors under routine operation using small cubic low-Carbon stainless steel samples.
Matsubayashi, Masahito; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.384 - 388, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Sato, Hiroshi; Kaminaga, Masanori; Hino, Ryutaro; Monde, Masanori*
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 2, p.935 - 944, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Watanabe, Noboru; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.657 - 666, 2003/07
Neutronic design studies were carried out on the J-PARC coupled H moderator. The highest time- and energy- integrated intensity below 15 meV, pulse peak intensity at 2 meV and 10 meV, were given by 100% para-H
moderator. The highest time- and energy- integrated intensity below 15 meV, pulse peak intensity at 2 meV and 10 meV, were given by 100% para-H moderators, but the optimal moderator thickness was different for each: more than 220 mm, about 120 mm and 80 mm, respectively. Finally, we concluded 140 mm was the optimal thickness for the 100% para-H
moderators, but the optimal moderator thickness was different for each: more than 220 mm, about 120 mm and 80 mm, respectively. Finally, we concluded 140 mm was the optimal thickness for the 100% para-H coupled moderator. Cold neutron distributions on the moderator viewed surface were found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. This rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use. The intensity decreases along with beam-extraction angle to the normal direction down to about 70% at 25.4
coupled moderator. Cold neutron distributions on the moderator viewed surface were found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. This rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use. The intensity decreases along with beam-extraction angle to the normal direction down to about 70% at 25.4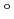 . Then, we propose a cylindrical shape coupled moderator which brings about a slight intensity decrease for 0
. Then, we propose a cylindrical shape coupled moderator which brings about a slight intensity decrease for 0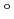 but a increase in the averaged intensity over the angles of interest.
but a increase in the averaged intensity over the angles of interest.
 range for International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF)
range for International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF)Nakamura, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho*; Nakamura, Hideo; Takeuchi, Hiroshi; IFMIF International Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 65(3), p.467 - 474, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)IFMIF is an accelerator-based neutron source for development of fusion materials. The Li target system consists of a target assembly, a Li purification system and various diagnostics. An intense deuterium beam power up to 10 MW in a footprint of 20 5 cm
5 cm corresponds to ultra high heat flux up to 1 GW/m
corresponds to ultra high heat flux up to 1 GW/m . To handle such an ultra high heat flux, the high-speed liquid Li flow with a velocity of 20 m/s and a concave flow configuration are necessary. According to thermal-hydraulic analysis, an induced centrifugal force (160 G) under the concave back wall of a radius of 25 cm is sufficient for IFMIF operation. To confirm the hydraulic characteristics of Li flow, water jet experiment has been done. Moreover, validation experiment in Li loop is planned. In addition, to control tritium and impurities such as C, N, O below permissible levels, a cold trap and two hot traps are used. These technologies have similarities in plasma facing components in fusion reactor. In presentation, the IFMIF Li target technology and its application of to the plasma facing component will be discussed.
. To handle such an ultra high heat flux, the high-speed liquid Li flow with a velocity of 20 m/s and a concave flow configuration are necessary. According to thermal-hydraulic analysis, an induced centrifugal force (160 G) under the concave back wall of a radius of 25 cm is sufficient for IFMIF operation. To confirm the hydraulic characteristics of Li flow, water jet experiment has been done. Moreover, validation experiment in Li loop is planned. In addition, to control tritium and impurities such as C, N, O below permissible levels, a cold trap and two hot traps are used. These technologies have similarities in plasma facing components in fusion reactor. In presentation, the IFMIF Li target technology and its application of to the plasma facing component will be discussed.
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Hino, Ryutaro; Monde, Masanori*
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2003/04
no abstracts in English